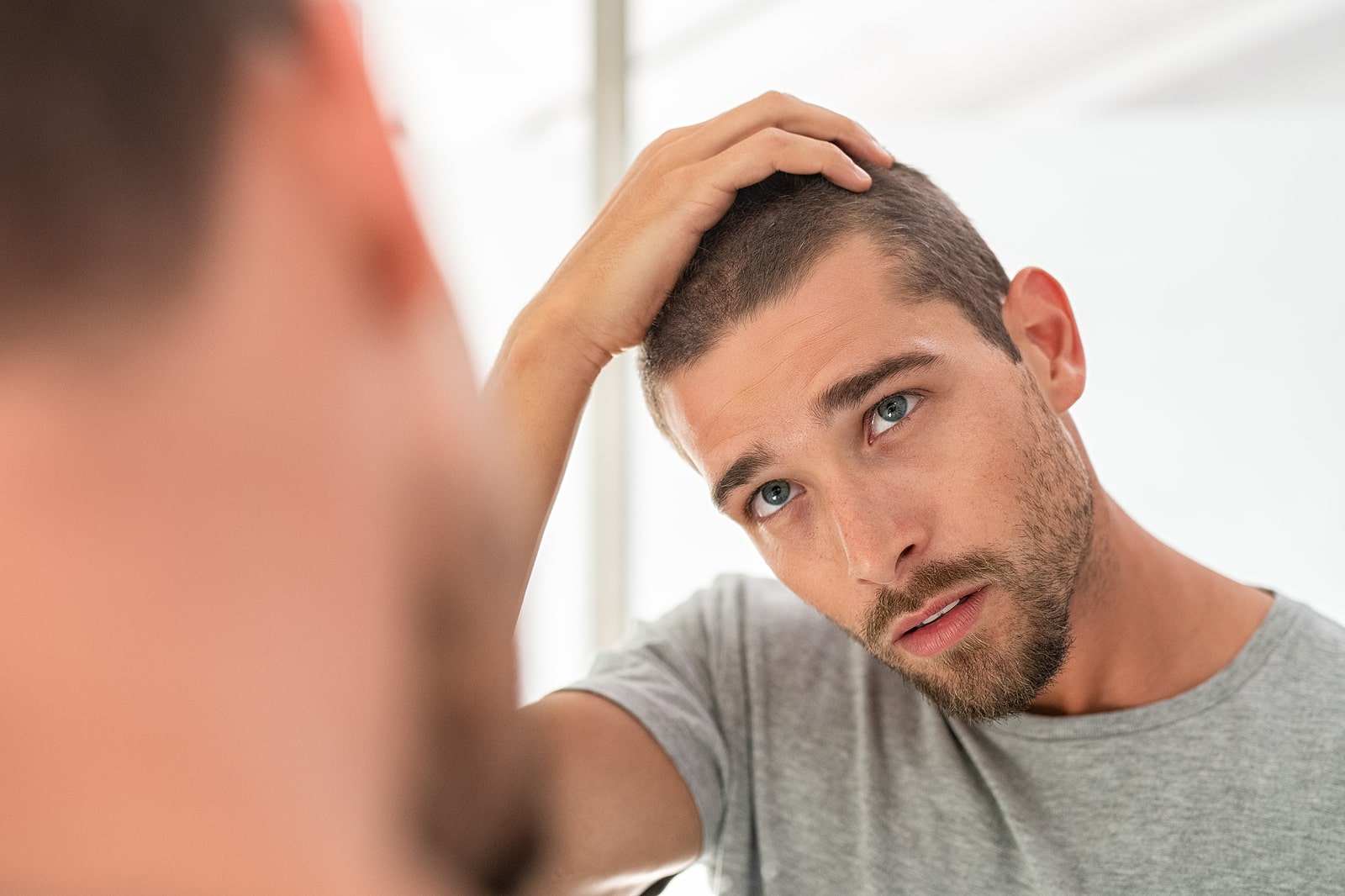
Hair loss affects many people at some point in their lives. There are lots of possible causes for hair loss, some of which are totally natural and normal. According to a 2020 study, about 12.42 million Americans used some sort of hair growth product during the year. While hair loss is common, it can cause some people anxiety and prompt them to look for hair growth solutions. Read on for more on some common types and causes of hair loss.
Common types of hair loss
Androgenetic alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common type of hair loss. It affects over 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States. More common in older adults, androgenetic alopecia can occur at any point after puberty. It is thought to be related to hormones and can be treated with hair growth medication. There are two types of androgenetic alopecia: male and female pattern hair loss.
Some possible contributing factors include:
- Iron deficiency
- Excess vitamin A
- Severe chronic illness
- Malnutrition
- Use of blood thinners
- Abnormal quantity of protein in the scalp
Male pattern hair loss
Men generally begin to lose hair due to interactions between the following three factors:
- Genetics
- Age
- Hormones
Hair loss in men is caused by the gradual shrinkage of tiny cavities in the skin at the base of hair strands known as scalp hair follicles. Hair begins to grow progressively shorter and finer until growth stops all together. Male pattern hair loss affects up to half of all white men by the age of 50 and up to 80% of men in the same group. Men of other ethnicities are often less affected. Chances of genetic male pattern hair loss increase drastically in men with first- and second-degree relatives who have experienced hair loss themselves.
Female pattern hair loss
Many women experience some level of hair loss. It is thought to be genetic and can be inherited from either parent. It often develops after menopause but can occur at any point after puberty. While genetics are the most common cause, female pattern hair loss can be caused by various medical conditions and can be a side effect of a medication, especially those used to treat cancer. Some simple prevention steps include:
- Incorporating proteins, irons, and essential oils into your diet
- Limiting heat styling and other damaging
- Protecting hair from sun damage
- Avoiding brushing hair when it is wet
Telogen/anagen effluvium
Effluvium hair loss refers to a type of hair loss that occurs when there is a change in the number of hair follicles growing hair. There are two types of effluvium: telogen and anagen.
If the amount of hair follicles producing hair decreases significantly during the resting (telogen) phase, there will be a substantial increase in dormant-stage (telogen) follicles. The result is shedding, or telogen effluvium hair loss. Telogen effluvium appears as a diffuse thinning of hair on the scalp, which might not be even all over. Usually, the hair on the top of the scalp thins more than it does on the sides and back. Hair line recession is an uncommon side effect but can occur in rare chronic cases.
Anagen effluvium occurs due to acute injury to the hair follicles by an endogenous or exogenous cause. It is defined by sudden shedding of structurally damaged hairs during the growth (anagen) stage of the hair cycle. Hair loss is usually quite rapid and can occur in other parts of the body, such as the eyebrows and eyelashes. Anagen effluvium can affect people of any age, sex, or race. Symptoms can be brought on by the following:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation
- Fungal infections
- Autoimmune conditions
Both telogen and anagen effluvium are treatable via medication. Many people choose to explore hair restoration or cosmetic camouflage options before hair grows back.
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is a condition which causes hair to fall out in patches, which can start out unnoticeable. It develops when the immune system attacks the hair follicles, resulting in hair loss on the scalp and other parts of the body. It often develops slowly and recurs after years between incidents. In some cases, the condition results in totally hair loss, called alopecia universalis. This condition prevents hair from growing back. The extent of hair loss and regrowth in people affected by alopecia varies from person to person.
Unfortunately, there is not yet a known cure for alopecia areata. However, there are a variety of treatments available that may encourage hair regrowth and prevent future hair loss. Topical treatment, injections, and various forms of therapy are available. Some natural remedies include:
- Acupuncture
- Microneedling
- Probiotics
- Vitamins
- Scalp massage
- Essential oils
- Herbal supplements
If you are interested in hair regrowth solutions, it is best to contact a hair restoration specialist.
Causes of hair loss
Pregnancy or menopause
Hormonal changes caused by pregnancy can sometimes cause different levels of hair loss. Rising estrogen levels slow down the natural cycle of hair follicle shedding. Physical stress and iron deficiencies common during pregnancy can also cause hair loss. Some people even experience hair loss during the months after giving birth due to the sudden decrease in estrogen levels.
During menopause, some people notice a change in hair pattern. Condition, rate of hair growth, and volume of hair may change. Hair loss is very normal during menopause across all ethnic groups due to age, genetics, and acute physical stress.
Hair loss due to pregnancy or menopause can be improved by cosmetic practices, i.e.:
- Reducing the use of heat styling tools
- Using hair-thickening products
- Hair regrowth topical solutions
- Laser therapy
- Hair systems
- Hair restorations
Medications
Some common types of medication can cause hair loss by interfering with the normal cycle of scalp hair growth, such as:
- Mood stabilizers
- Birth control pills
- Antibiotics
- Epilepsy drugs
- Blood pressure medications
- Steroids
- Chemotherapy drugs
It is important to review any medications you take and discuss side effects with your doctor. When hair loss does occur as a result, there is a good chance it will eventually grow back. Treatment options that stimulate hair regrowth are also available.
Emotional or physical distress
You may notice sudden hair loss during a particular stressful period. Hair can start to fall out in bed, in the shower, when your brush it, and at other random times. Losing a loved one, going through surgery, or being diagnosed with an illness can increase your risk of hair loss. In most cases, excess shedding begins 2 to 3 months after a stressful physical or emotional event. It usually peaks about 4 to 5 months later and goes back to normal within 6 to 9 months.
Diet/nutritional deficiencies
Hair loss can occur due to nutritional deficiencies. Diets that are too low in protein and certain vitamins, such as iron, can cause excessive shedding. Essential fatty acids play a major role in the health of your hair. Some foods that are rich in omega-3s include:
- Salmon
- Tuna
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Canola oil
- Walnuts
- Soybeans
- Tofu
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Brussel sprouts
Foods containing Vitamin B6, B12 and folic acid are also critical to healthy hair. Examples include:
- Bananas
- Potatoes
- Spinach
- Poultry
- Dairy products
- Citrus fruits
- Beans
- Fortified grains
Contact us
If you are struggling with hair loss or would simply like to consult with a professional, contact us today or call (410) 931 3399. We provide high-quality hair restoration and hair system services to the Baltimore, Maryland community.