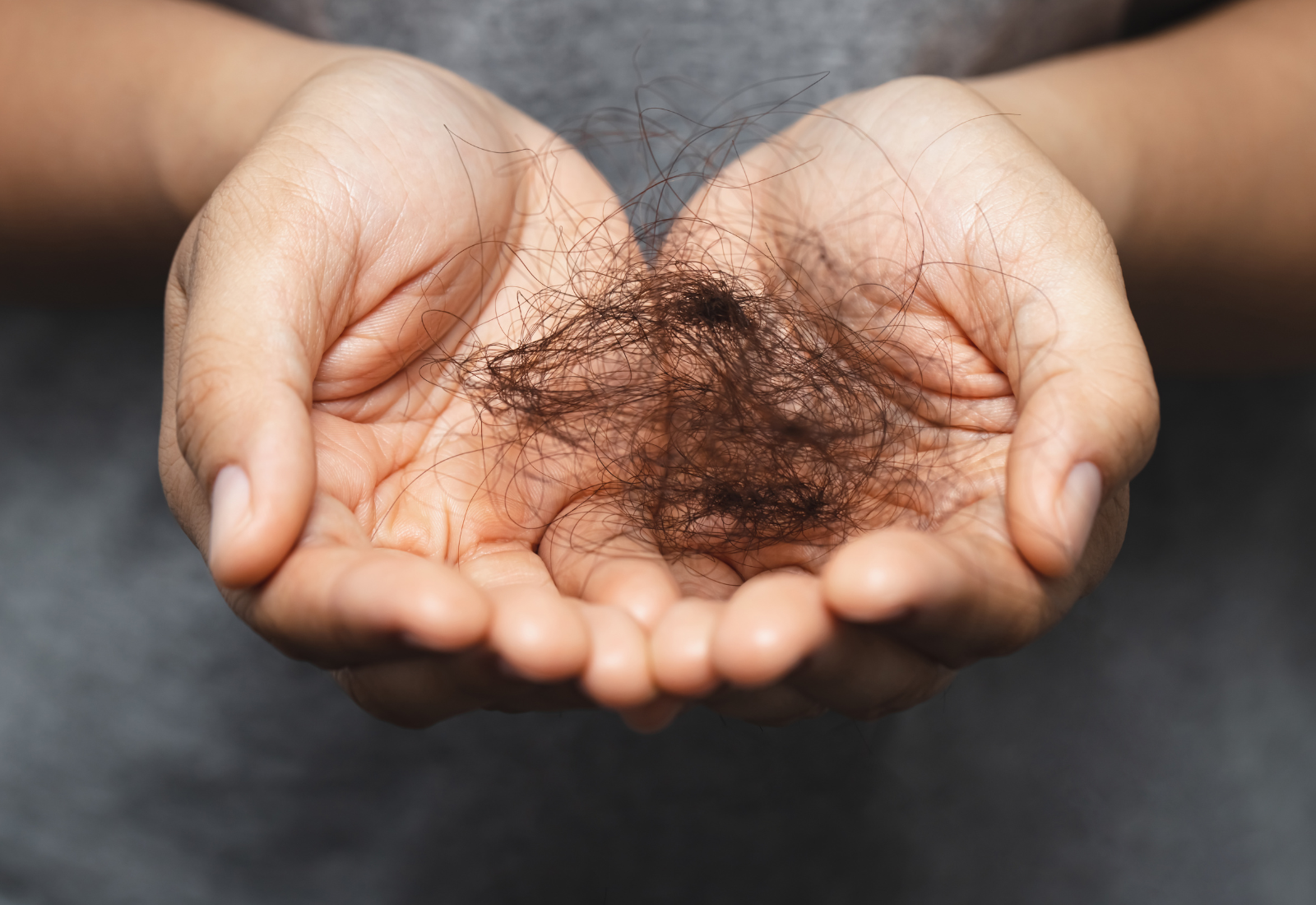
Trichotillomania, also known as hair-pulling disorder, is a condition characterized by the irresistible urge to pull out one’s hair. This disorder can lead to significant distress and impairment in various aspects of life. Understanding trichotillomania is essential for individuals affected by it, as well as their loved ones, to provide adequate support and seek effective treatment options.
What is Trichotillomania?
Trichotillomania is classified as an impulse control disorder, where individuals experience an overwhelming urge to pull out their hair. This can occur from any part of the body where hair grows, such as:
- The scalp
- Eyebrows
- Eyelashes
- Beard or facial hair
- Pubic region
- Body hair (such as arms, legs, or chest)
The pulling often provides a sense of relief or gratification, but it is usually followed by feelings of guilt, shame, or regret.
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of trichotillomania is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Stress, anxiety, boredom, and other emotional triggers can exacerbate the urge to pull hair. Additionally, certain personality traits, such as perfectionism or impulsivity, may contribute to its development. It is estimated that about 5-10 million Americans suffer from trichotillomania.
Effects of Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania’s impact extends beyond mere physical appearance, delving into the emotional and psychological realms, significantly affecting an individual’s quality of life.
Physical Consequences
The physical ramifications of trichotillomania can be distressing. Persistent hair pulling can result in noticeable bald patches across the scalp or other affected areas, causing discomfort and often leading to difficulties with self-image. In severe cases, individuals may develop the following:
- Skin irritation
- Inflammation
- Infections
- Scalp sensitivity
- Hair follicle damage
Emotional Distress
The emotional toll of trichotillomania can be profound and pervasive. Constantly grappling with the urge to pull out hair and the subsequent feelings of guilt and shame can erode self-esteem and confidence. The visible effects of hair loss may trigger embarrassment and self-consciousness, leading individuals to withdraw from social interactions and avoid situations where their condition may be noticed or scrutinized. This social withdrawal can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and isolation, further perpetuating the cycle of distress.
Psychological Impact
Trichotillomania often coexists with other mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. The chronic stress of managing the urge to pull hair and the resulting consequences can contribute to heightened levels of anxiety and exacerbate symptoms of depression. Additionally, the cyclical nature of trichotillomania, characterized by periods of hair pulling followed by feelings of regret and attempts to conceal the behavior, can perpetuate a sense of helplessness and frustration.
Coping Strategies
Managing trichotillomania requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and triggers while providing practical tools for managing the urge to pull hair. Here are several coping strategies that individuals can incorporate into their daily lives:
Mindfulness and Acceptance-Based Approaches
Mindfulness-based interventions, such as mindfulness meditation and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), offer valuable tools for individuals grappling with trichotillomania. These approaches promote greater self-awareness, emotional regulation, and acceptance of difficult experiences. Key strategies include:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Engaging in regular mindfulness meditation practices, such as focused breathing or body scan exercises, cultivates present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance of thoughts and sensations.
- Observing Urges Non-Judgmentally: Through mindfulness practices, individuals learn to observe the urge to pull hair without reacting impulsively or harshly judging themselves. By adopting a curious and compassionate stance towards their experiences, individuals develop greater resilience in managing difficult emotions.
- Defusion Techniques: ACT teaches individuals to “defuse” unhelpful thoughts and beliefs by viewing them as transient mental events rather than absolute truths. By creating distance from distressing thoughts, individuals can reduce their impact on behavior and cultivate psychological flexibility.
- Committed Action: ACT emphasizes the importance of taking committed action towards valued goals, even in the presence of discomfort or uncertainty. By aligning actions with values, individuals with trichotillomania can pursue a rich and fulfilling life, transcending the limitations imposed by their condition.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is widely regarded as the gold standard in treating trichotillomania. This therapeutic approach focuses on identifying and challenging the distorted thoughts and beliefs that contribute to hair pulling behaviors. Through cognitive restructuring techniques, individuals learn to recognize and reframe negative thought patterns associated with trichotillomania.
Habit Reversal Training (HRT)
HRT is a behavioral therapy specifically designed to address repetitive behaviors like hair pulling. This technique involves identifying triggers for hair pulling and implementing competing responses to interrupt the urge. By replacing the habitual act of pulling with a more constructive behavior, such as:
- Clenching fists
- Engaging in relaxation exercises
- Squeezing stress balls
- Using fidget toys
- Applying pressure to the scalp
- Engaging in physical activity
- Deep breathing
Support Groups and Peer Support
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with trichotillomania can provide invaluable support and validation. Joining support groups allows individuals to share their experiences and receive encouragement from peers who are facing similar struggles. Peer support can foster a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation. This can empower individuals to navigate their journey towards recovery with greater resilience and hope.
Professional Support and Treatment
Seeking professional help from qualified mental health professionals is essential for effectively managing trichotillomania. Psychologists, psychiatrists, and counselors can provide assessment, diagnosis, and evidence-based treatment options tailored to the individual’s needs.
In severe cases of trichotillomania where hair loss is significant, consulting with a hair restoration specialist for services such as hair transplants, hair systems, human hair wigs, hair extensions, or laser hair therapy may be beneficial in restoring confidence and self-esteem.
Contact Eldorado Hair Restoration Center
If you or someone you know is struggling with trichotillomania and experiencing hair loss, Eldorado Hair Restoration Center offers comprehensive solutions in Baltimore, MD. Our team of experienced professionals specializes in hair restoration services. Contact us today to schedule a free hair analysis and explore the best Baltimore hair loss solutions tailored to your needs.